
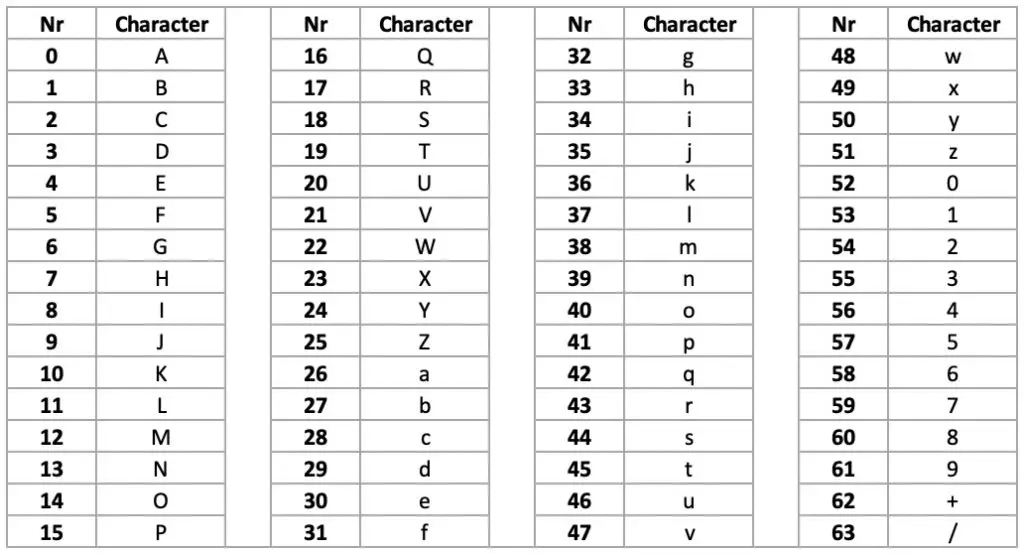
The simplest way to Base64 encode a string in Java is by using the basic encoding scheme. Let us start with the basic encoding example. Now it is time to do the actual Base64 encoding in Java by using the Base64 class. The decoder ignores all line separators or other characters not found in the base64 Alphabet. Every line, except the last line, is separated from the next line by using a carriage return \r followed by a linefeed \n. The encoded output is represented in lines of no more than 76 characters each. MIME - The MIME variant uses the Basic Base64 Alphabet (characters from a-z, A-Z, 0-9, /, and +) for encoding and decoding operation.The decoder rejects the data if it contains characters outside of a-z, A-Z, 0-9, -, and _ (known as URL and Filename safe Base64 Alphabet). No line feed character is added by the encoder. URL and Filename safe - This is very much similar to the Basic Base64 encoding except that + and / symbols are replaced with - and _ respectively to make the output URL and filename safe.If there are characters outside of the Base64 alphabet, the decoder rejects the data. The encoder does not add the line feed character. Basic: - This is the standard Base64 encoding that only uses a-z, A-Z, 0-9, /, and + characters (also called The Base64 Alphabet) for encoding and decoding operation.The Base64 class was introduced in Java 8 and it supports the following variants of Base64 as specified in RFC 4648 and RFC 2045: This class provides static methods to get encoders and decoders for the Base64 encoding scheme.
#BASE64 ENCODING JAVA HOW TO#
In this article, you'll learn how to perform Base64 encoding and decoding by using the Base64 class in Java. It is primarily used to transfer content-based messages over the Internet. Base64 is a binary-to-text encoding scheme that describes binary data in an ASCII string format by translating it into a radix-64 representation. UnsupportedEncodingException import java. The decoder ignores all line separators and other characters not found in the basic base64 alphabet. Each line (except the last line) is separated from the next line via a carriage return (\r) followed by a linefeed (\n). The encoded output is organized into lines of no more than 76 characters. MIME enforces a limit on line length of Base64 encoded data. MIME: The MIME variant uses the Basic Base64 alphabet ( A-Za-z0-9+/). The decoder rejects data that contains characters outside A-Za-z0-9-_. URL and Filename Safe: It is same as the Basic Base64 encoding except that + is replaced by - and / is replaced by _ to make the output URL and filename safe. The decoder rejects data that contains characters outside this set. The algorithm converts the input to a set of characters containing A-Z, a-z, 0-9, + and /.

Basic: This is the standard Base64 encoding defined in the RFC 4648.Java 8’s Base64 API contains implementations for all the Base64 encoding and decoding variants described in the official RFC 4648.įollowing variants of Base64 encoding and decoding is supported. In this article, you’ll learn how to Base64 decode any Base64 encoded text back to binary data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
